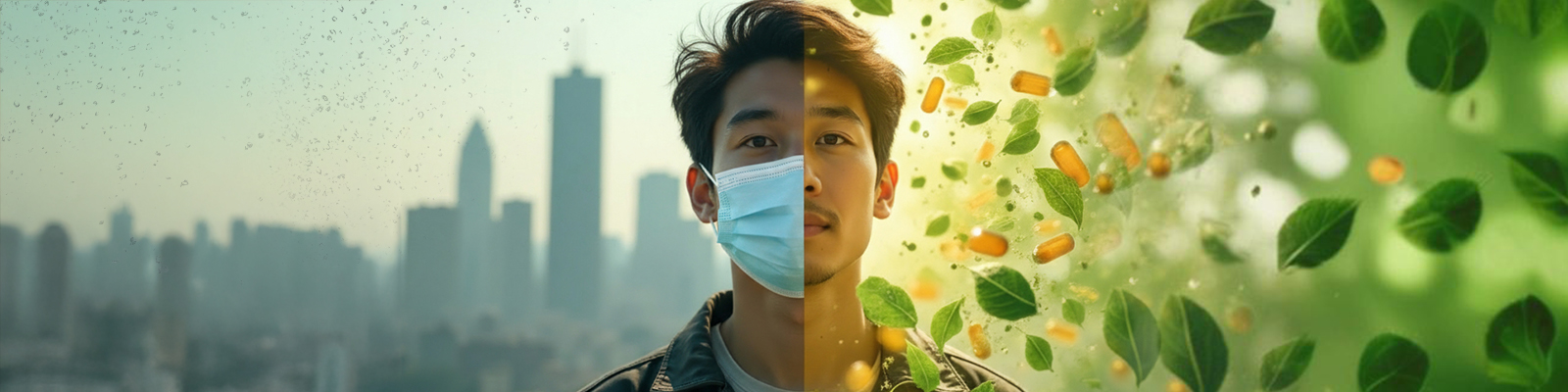
The air pollution challenge is one of the greatest preventable air quality hazards undermining humanity at large. Fine particles and gases of polluted air—particularly PM2.5 (particles up to 2.5 microns in diameter)—may penetrate deep into the lungs, enter the bloodstream, set up an inflammatory reaction, oxidative stress, and an array of negative mechanisms against the heart, lungs, and brain.
In India, the burden is especially dire. The India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative found that air pollution was responsible for 1.67 million deaths in 2019 — almost 18% of total deaths across the country. Moreover, studies indicate that one in every three children in Delhi already has compromised lung function due to long-term exposure to bad air. This underlines the need for immediate protective action, even as policy reform and cleaner technologies are the longer-term options.
Source: The Lancet Planetary Health / Centre for Science and Environment (CSE)
In addition to preventing exposure (masks, purifiers, avoiding routes along heavily trafficked main roads), there has been recent research supporting nutraceuticals – vitamins, minerals, fatty acids and supplements aimed at suitable body defence against pollution-induced harms.
Below is a summary of the evidence, suggested practical considerations, and clear health warnings.
Why nutraceuticals may help
Air pollution causes damage to tissue via two primary biological mechanisms: oxidative stress (overabundant reactive oxygen species) and inflammation. Antioxidant nutraceuticals may eradicate free radicals, and anti-inflammatory modulating agents that lessen an aberrant immune over-activation. There is quite a lot of commonly adopted clinical and experimental evidence that shows that in specific circumstances supplementation may lessen indices of oxidative stress, benefit lung function indices, or lessen indices of inflammatory mediators in humans exposed to air pollution.
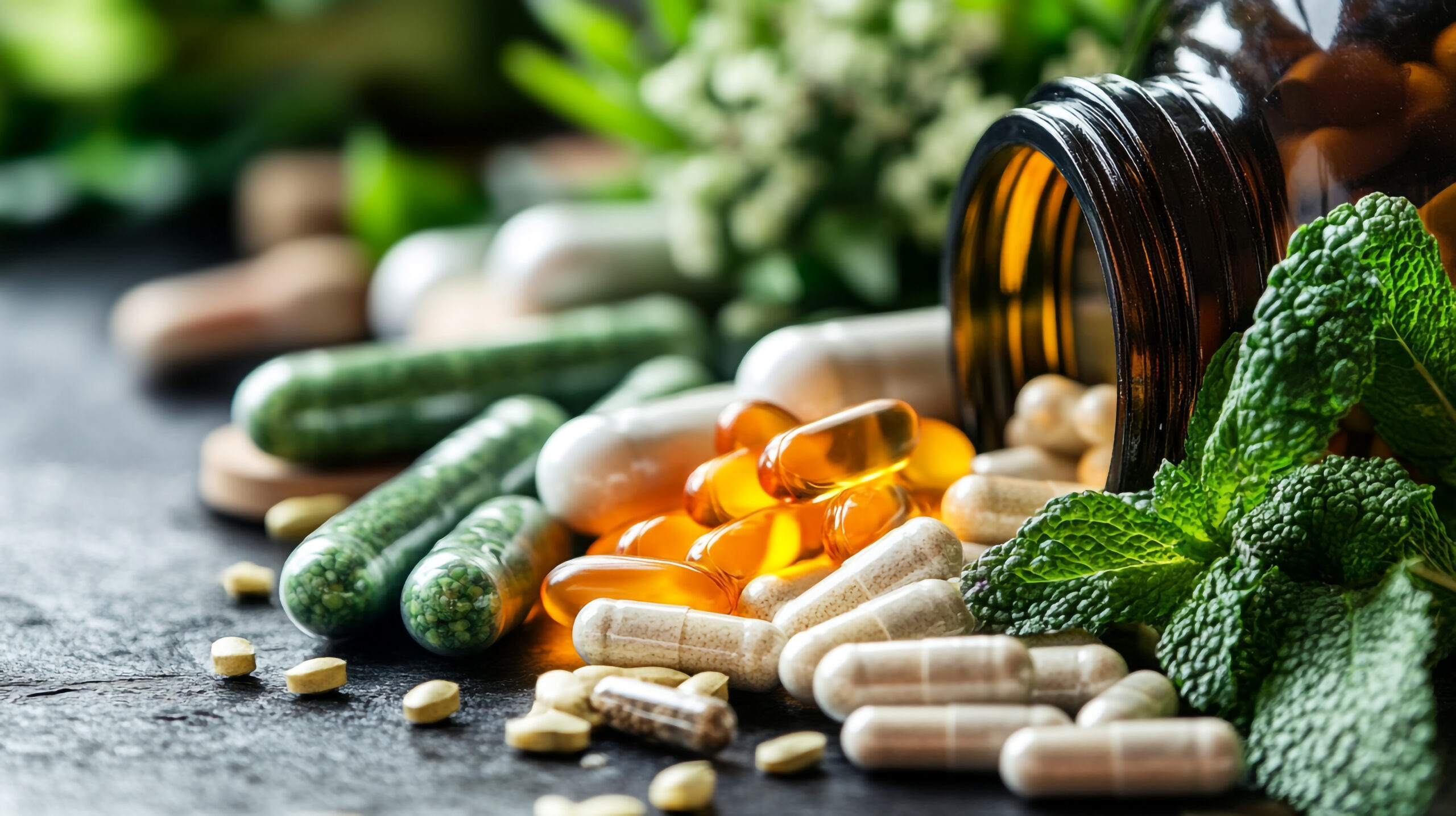

Image Credit: Free Pik
Nutraceuticals with the best evidence
Antioxidants (vitamin C, vitamin E, and related molecules)
Vitamin C and vitamin E are among the most effective antioxidants. Clinical and experimental data indicate that antioxidant supplementation decreases oxidation indices after exposures to short-term pollution and is beneficial to lung function indices in at-risk groups (children, the elderly, and asthmatics). These vitamins remove free radicals or reactive oxygen species and maintain intracellular antioxidant machinery to prevent damage from free radicals.
A practical note: Vitamin C should be obtained in a diet rich in citrus, berries, and peppers, and supplementation should only be considered if there is low dietary intake. In the studies we reviewed, usual supplemental doses of vitamin C constituted moderate amounts taken daily: 500–1,000 mg. Unless recommended by a health professional, avoid megadose.
Source : NIH Office of Dietary Supplements – Vitamin C Fact Sheet for Health Professionals
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) NAC is an important precursor to glutathione, the main intracellular antioxidant in the body. Clinical and mechanistic studies show NAC restores glutathione and reduces oxidative lung damage caused by toxins. NAC is used to treat certain conditions affecting lung function to help liquefy and decrease mucus.
Practical note: NAC has been studied extensively in doses ranging from 600-1200 mg a day in clinical trials; health professionals should be consulted before considering the initiation of supplement therapy, especially if the patient is taking blood thinners or has any histories of long-term conditions.
Source: National Institutes of Health (NIH) – LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Omega-3 Fatty Acids The anti-inflammatory effects of Omega-3s (EPA and DHA) are well established. Many randomized studies, and many population studies, indicate that greater intake of omega-3s is helpful in pollution-induced inflammation, lower prevalence of risk factors for cardiovascular disease, and sometimes improved cardiovascular autonomic function which has been shown to decline after exposure to particulate matter.
Practical note: Aiming at getting it from dietary sources, such as fatty fish, or from a high-grade fish oil supplement is preferable. Doses used in studies differ quite a bit, but many trials go for 1-3 g of combined EPA+DHA daily. Consult with your physician if you are taking anticoagulants.
Source: Mayo Clinic / Drugs.com
Polyphenols and curcumin
Plant polyphenols, such as those in green tea, berries, and turmeric, are known to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Curcumin (the active ingredient in turmeric) has been evaluated in animals and small studies in people and showed effectiveness in preventing oxidative stress associated with pollution. Formulations that enhance bioavailability of curcumin will produce a greater response.
Practical advice: try to consume polyphenol-based foods every day. You can take a standardized curcumin supplement, at a dose shown to have bioavailability, if you want to consume more polyphenols in a concentrated manner.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a key modulator of immune function and can change the risk of respiratory infections and inflammatory response. Generally, observational data point to poorer outcomes when pollution is present and there is compromised vitamin D status, while the intervention data do not show consistency.
Practical advice: get your blood levels taken by your doctor; supplement just to achieve sufficiency; don’t just take random high levels.
Who profits most?
Individuals with existing respiratory or cardiovascular illness, older persons, children, pregnant individuals, workers exposed outdoors, and individuals living in heavily polluted urban areas are most likely to benefit from reduced combined exposures plus targeted nutraceutical support. For otherwise healthy adults, an antioxidant-rich, omega-3-dense diet is a logical, low-risk option.
Safety and realistic expectations
Nutraceuticals are not cures, but rather adjuncts. They lower biological stress and perhaps decrease short-term risk, but do not eliminate pollutants or substitute for public-health protocols. Supplements can interact with drugs and can be contraindicated in certain diseases. New regimens, particularly high-dose treatments such as NAC or omega-3 at therapeutic doses, should always be preceded by consultation with a health professional.
Practical daily schedule (example)
- Eating first: colorful fruits and vegetables, fatty fish twice a week, green tea, turmeric-spiced foods.
- Supplement foundation if necessary: vitamin C (moderate amount), an omega-3 supplement (1 g+EPA+DHA), vitamin D if low.
- Targeted therapy for very high risk: talk to your clinician about NAC or curcumin.
- Exposure reduction: masks on high-pollution days, indoor air filtration, and avoiding heavy-traffic exercise routes.
Zeon Lifesciences contribution to respiratory health solutions
Cleaner air is the end point, but the fact remains that millions still breathe dirty air today.
At Zeon Lifesciences, we realize that protecting respiratory health today is an urgency. As a global leading third-party contract manufacturer in the nutraceutical industry, we have expertise in developing innovative, research-driven solutions to fortify the body against environmental stressors.
One of our main products is protein powder with added essential vitamins, minerals, prebiotics, probiotics, NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine), and curcumin — all specifically created to enhance respiratory wellness. This very special blend brings together the strength of protein for muscle and immune support with specific nutraceuticals that are proven to fight oxidative stress, decrease inflammation, and build lung immunity.
By joining forces with Zeon Lifesciences, brands can provide top-notch, science-based respiratory wellness products to consumers — enabling them to breathe a little more comfortably, even when the air quality is questionable.
References
- Calder, P. C. (2017). Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: From molecules to man. Biochemical Society Transactions, 45(5), 1105–1115. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20160474
- Romieu, I., Castro-Giner, F., Kunzli, N., & Sunyer, J. (2008). Air pollution, oxidative stress and dietary supplementation: A review. European Respiratory Journal, 31(1), 179–197. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00128106
- Kelly, F. J., & Fussell, J. C. (2015). Air pollution and public health: Emerging hazards and improved understanding of risk. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37(4), 631–649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9720-1
- Heo, J., Kim, H., Lee, D., & Lim, Y. (2018). N-acetylcysteine attenuates diesel exhaust particle-induced lung inflammation by modulating oxidative stress-related pathways. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 41(6), 3472–3484. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3515
“Good Health for All”
Zeon is serving with over three decades of experience in the industry, we are working meticulously to bring knowledge of nature with innovation and advanced technology in the form of unique combinations to our consumers. Our in-house formulae and manufactured products are for all age groups in various SKUs such as Powders, Diskettes, Tablets, Capsules, Oral liquids, Caplets, Sprays, Drops, Herbal Juices, etc.WHY CHOOSE ZEON?
State-of-the-art manufacturing facility in Himachal Pradesh spread over 28000 sq yds 4 manufacturing units under integrated complex Serving quality products since 1987 GMP certified facility
NSF Registered
DSIR- recognized R&D Lab
NABL Accredited Quality testing
USFDA Registered
Great place to work certified
Food safety award from CII
1200+ formulations
800+ Active SKUs
30+ Recognitions
15+ Accreditations
Exclusive diskette manufacturing facility
Exclusive spray drying and dry blended powders manufacturing facility